With a total market cap of almost $1 trillion and over 20,000 different crypto tokens, the cryptocurrency market is nothing to sneeze at. In fact, over the last ten years, the crypto world has produced so much innovation and value that it has redefined finance forever.
One significant change that has brought is the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi). In particular, the popularity and diversification of crypto coins have increased the demand for decentralized exchanges.
These DEXs aim to deliver reliable crypto conversion and trading services at advantageous exchange rates with lower trading fees. Their lack of intermediaries makes them an attractive alternative to traditional crypto exchanges like Coinbase or Binance.
But what if you can’t wrap your head around what decentralized exchanges even are? Pretty much everything about them sounds complicated.
Don’t you worry! This guide will demystify the term and turn you into a true DEX expert in no time. We’ll discuss:
- What decentralized exchanges are;
- How they work;
- What sets them apart from their centralized counterparts;
- What kinds of DEXs exist;
- What are some of the most popular DEXs at the moment, and how to use them?
Read until the end to see step-by-step guides on how you can exchange cryptocurrency on five select DEXs.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into the topic and see what a decentralized exchange really is.
What Is a DEX?
The term DEX is nothing but an abbreviation of ‘decentralized exchange.’ Considering what a mouthful the latter phrase is, you’ll note we use both terms to refer to the same thing in this guide.
But knowing what a word signifies is hardly the same as understanding it. So, what exactly hides behind the name decentralized exchange?
Let’s start with the more obvious first: a DEX is a cryptocurrency exchange. In other words, people visit DEXs to trade one crypto for another. For example, you can exchange bitcoins (BTC) for ether (ETH). Clear so far?
The word ‘decentralized’ is more complicated. It means that there is no central authority, regulator, or mediator to facilitate trades. As a result, DEXs are very different from more traditional crypto exchanges like Coinbase or Binance.
If you’re using one of those, the company is a middleman facilitating your trade. Moreover, they have CEOs and other staff that make decisions about the exchange, its terms and conditions, etc., and users have no control over that process.
Instead, DEXs go around this problem by relying on blockchain-supported peer-to-peer (P2P) technology. By that, we mean that:
- Decentralized exchanges run on blockchains, and
- People trade cryptocurrencies freely amongst each other through self-executing smart contracts.
Most decentralized exchanges run on Ethereum. But, of course, non-Ethereum DEXs exist, and we will provide examples further on in this guide. In any case, all decentralized crypto exchanges run on a distributed network and require an Internet connection to work.
Because DEXs enable people to make direct crypto transactions with one another, they fall under the umbrella of ‘decentralized finance.’ Also known as DeFi, this section of the crypto world includes all apps and inventions that provide financial services in a decentralized manner.
How Does a DEX Work?

The first thing you need to understand about decentralized exchanges is that they only work with crypto. Fiat currency (i.e., traditional money) is not welcome here.
The main reason is that as soon as you introduce fiat money into the equation, you involve one regulatory body or other. Money comes from a bank account or a credit/debit card linked to one. And what are banks? Intermediaries. DeFi can’t allow that — which is its main advantage.
As a result, decentralized exchanges only allow users to trade one crypto coin or token for another. Each DEX uses its own algorithm to match users in a way that enables the deal to be executed.
For example, it can be a simple swap. Let’s say that Bitcoin was worth $20,000 and ether was $1,000, and you’re looking to change one BTC into ETH. At the same time, there is an ether seller using the same DEX, willing to sell their ether for BTC. They will agree to sell you 20 ETH for one BTC. If that exchange rate is acceptable to you, you can trade. That’s how P2P trading works.
But more commonly, crypto token owners would be depositing their assets into liquidity pools hosted by the DEX. Then, when you come to the platform to trade, the DEX will ‘grab’ tokens from the relevant liquidity pool and put yours there to perform the exchange.
Some DEXs can execute more complicated orders that might require multiple exchanges to give you the best price. Nevertheless, even then, the user only places a single order. It’s up to the blockchain to execute all the relevant operations and perform the trade.
Others still specialize in competitive trading, similar to how the Wall Street stock exchange works, for example. Only, they focus on crypto assets and derivatives alone and function entirely online.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Work?
- You (i.e., the Maker) create an order for your desired exchange.
- Using your unique key, you sign the order.
- The blockchain powering the DEX receives the order.
- Another user (a Taker) decides to fulfil your order.
- The Taker also signs the order with their own key.
- The DEX binds the deal in a smart contract and executes the trade.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Exchange
Now that you know how decentralized exchanges work, you might wonder how they compare to a typical CEX like Binance.
Don’t worry; we won’t keep you guessing much longer! We have prepared a simple comparison chart for you to learn about the core differences between these two types of exchanges and the pros and cons of each.
| Criterion | Centralized Exchange (CEX) | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) |
| Central Authority | The company itself. | None. |
| Who has custody of the funds? | The exchange. | The user. |
| Privacy | Users are NOT anonymous. | Users are anonymous. |
| Can you trade crypto to crypto? | Yes. | Yes. |
| Can you trade fiat to crypto? | Yes. | No. |
| Do they follow KYC and AML rules? | Yes. | Not necessarily. |
| Do they use smart contracts? | No. | Yes. |
| What is the liquidity like? | High liquidity. | Somewhat lower liquidity. |
| Services they offer besides cryptocurrency exchange: | Crypto CFD trading. | Staking, liquidity pools, other DeFi services. |
| Can it be hacked? | Yes, it happens from time to time. | Not really; the blockchain keeps it secure. But it’s not impossible. |
Different DEX Types
Not all decentralized exchanges are created equal. As time went by, people developed more and more ways to organize a DEX. Thus, there are different kinds of decentralized exchanges out there.
Order Book
Order book types of exchanges are the first variety of DEX to arise. They work by grouping all buy and sell orders for each listed asset. The most popular market price for the asset is then determined by the difference between the bid and ask prices. Only the order information is on the blockchain. All of the crypto tokens involved in the trade remain in the users’ wallets.
Some examples of order book DEXs include:
- ViteX
- Tomo DEX
- dYdX
- Binance DEX (the decentralized version of Binance)
- Nash Exchange
Swaps
This variety of decentralized exchange directly swaps tokens between users in a peer-to-peer manner. They do not need order books. In addition, the price of the assets available for trading is not based on spreads (like it is with order book DEXs). Instead, pricing is determined by liquidity pools or similar mechanisms.
Swap exchanges are generally a more recent invention compared to DEXs that use order books.
Examples of swap-based decentralized exchanges include:
- UniSwap
- SushiSwap
- Curve
- Balancer
- Gnosis
Aggregators
DEX aggregators differ significantly from the previous two categories. Instead of proposing entirely new exchanges, they pull data from already existing DEXs. Utilizing various algorithms, aggregators hope to offer the most satisfactory exchange rates by combining the listings of other DEXs.
The most prominent example of a DEX aggregator is 1inch.
The Most Popular DEXs
Are you beginning to see why decentralized exchanges are so popular? Their great diversity, high degree of anonymity, and potentially better exchange rates have made them an integral part of the DeFi space.
If you’re interested in trying the services of a DEX yourself, look no further! We have selected some of the most popular exchanges in existence and prepared step-by-step guides on how to use them.
Here is how you can make use of the best decentralized crypto exchanges currently available. We scoured the web to identify the top five most liked DEXs to introduce you to. Let’s look at what makes them so special, one at a time.
1. Uniswap

Uniswap is the most popular decentralized exchange in the world right now. Running on the Ethereum blockchain, it relies on liquidity pools for price setting and performs smart contract-bound P2P trades.
There is a great variety of crypto coins you can exchange on Uniswap. However, they are only of the Ethereum standard. In other words, you won’t find tokens that run on other blockchains here. Luckily, the majority of cryptocurrencies in modern use are Ethereum-based anyway.
Based on data on its own website, Uniswap is responsible for:
- More than $1 trillion in trading volume;
- Over 100 million transactions (since launch).
How Does Uniswap Work?
We can’t explain Uniswap without talking about liquidity pools first. After all, they are the basis of this DEX — without them, Uniswap would not exist.
A liquidity pool is essentially a large collection of crypto tokens. They are locked in a smart contract and sit ready for Uniswap users to borrow them. But where do these cryptocurrencies come from? Good question!
Crypto owners lend them to Uniswap. Whether these people have mined the crypto themselves or purchased them on an exchange, they agree to ‘donate’ them to Uniswap and lock them in a smart contract. In turn, Uniswap rewards these liquidity providers with a share of the trading fees and its own native token, UNI.
Thus, liquidity pools are a win-win for everyone. First, crypto coin owners get to make a passive income from their portfolio by lending it. They also participate in the governance of Uniswap thanks to their UNI tokens. Furthermore, Uniswap gets to run a successful exchange, and everyone else has the chance to exchange their crypto for the tokens offered in the liquidity pool.
In many ways, Uniswap is a system that keeps enriching and improving itself with continual use.
You can learn more about Uniswap in this Coin Bureau video:
How to Exchange Crypto on Uniswap
In the following section, we’ll show you how to complete a simple exchange of cryptocurrencies on Uniswap.
Step 1. Go to the Uniswap website.
Simply navigate to Uniswap from your browser of choice.
Step 2. Click on the Launch App button in the upper-right corner of your screen.
Note that you don’t need to register anywhere. After all, the whole point of using a DEX is to be anonymous — having an account would defeat the purpose.
You should now be looking at the Swap window. This is where you can specify your order details.
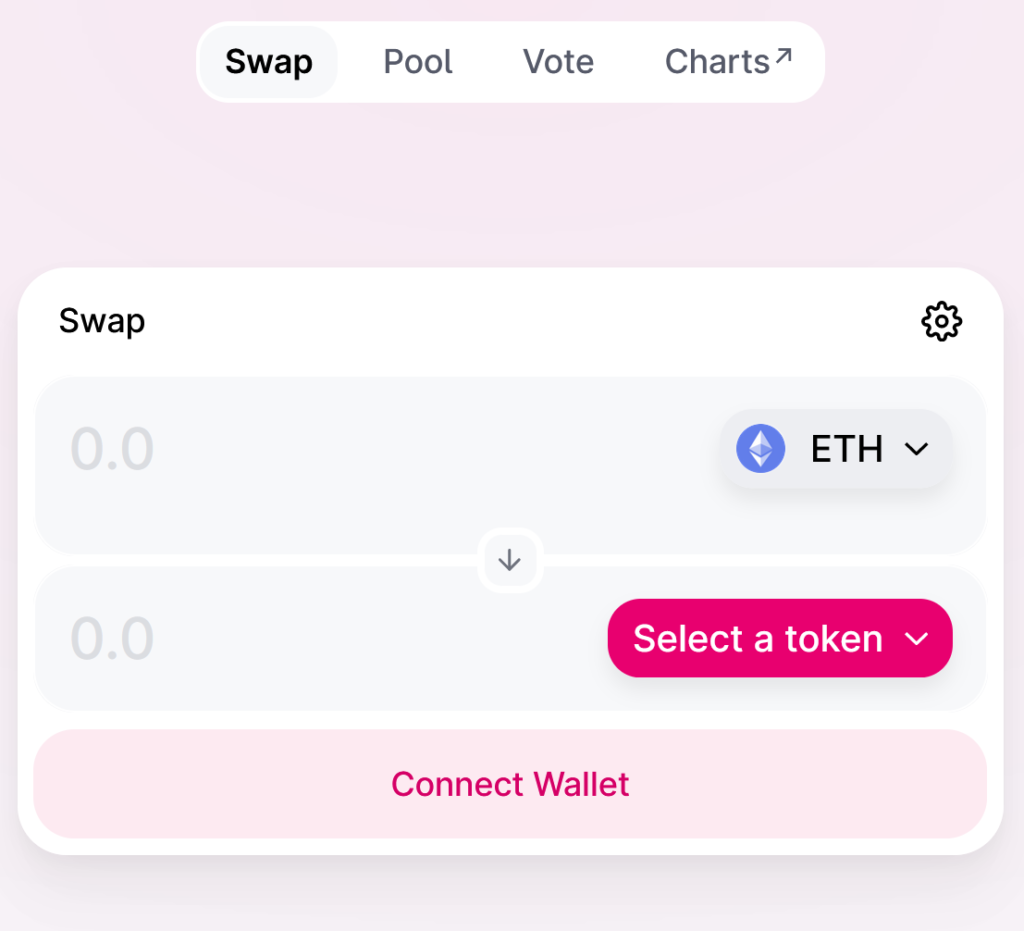
Step 3. Connect your crypto wallet to Uniswap.
To make the desired conversion, you need to take a crypto coin from your own wallet and swap it for another token from Uniswap’s LP. You’d also need to pay a trading fee (gas) for the transaction. For this reason, Uniswap needs to connect to your crypto wallet and make the relevant modifications.
When you click on the Connect Wallet button, you’ll be presented with several options.
Choose the option that applies to you and follow the on-screen instructions to link it to Uniswap.
Step 4. Set up the exchange you wish to make.
With your crypto wallet connected, you can now make a swap. If you press on the ETH icon, you’ll see a dropdown menu with other tokens to choose from. For the purposes of this guide, we’ll stick to Ethereum.

In the To field, use Select a token to choose the crypto you want to buy.
With both of your assets selected, go back to the From field and enter how much of your base cryptocurrency you’d like to use.

Uniswap will automatically calculate how much of the other cryptocurrency you’ll receive in the exchange. The platform will also let you know if you don’t have enough of the base crypto to fulfill the transaction.
Step 5. Confirm your swap.

If you have enough balance to cover the exchange and the gas fees, instead of ‘Insufficient ETH balance,’ you will see a bring Swap button. Pressing it will finalize the trade.
2. dYdX

dYdX is yet another popular choice of a decentralized exchange. Thanks to its innovative technology, it doesn’t focus on competing with the other DEXs on this list.
Instead, dYdX brings an altogether different utility. In particular, it specializes in offering crypto margin trading and perpetual contracts trading via its trading platform:
- Crypto margin trading refers to using leverage. In practice, this means that users borrow funds greater than their deposits to trade at a higher volume. Margin trading can generally lead to both higher profits and higher losses. Thus, it’s a high-risk, high-reward type of speculation.
- Crypto perpetual contracts are quite similar to futures. Futures represent a binding agreement between two parties to make an exchange for a certain price at a given date. Perpetuals, as the name suggests, have no fixed date, so you can postpone settling indefinitely. Thus, you can close this type of position when the asset’s price is most suitable for you.
More exciting things are coming to dYdX, with it recently announcing a new chain:
How Does dYdX Work?
Like Uniswap, dYdX makes use of liquidity pools. However, this DEX uses a different structure to facilitate margin and perpetual contract trading. Without boring you with technical details, suffice to say that liquidity here comes from the collateral of all traders using dYdX.
Of note is also that dYdX uses two separate layers. Layer 1 runs on Ethereum and supports trading all compatible coins and tokens. The maximum leverage is 5x, and the overall performance depends on how busy the Ethereum network is. As of June 2022, Layer 1 is the inferior part of dYdX.
Layer 2 is far better. It runs on StarkWare and is both faster and cheaper to use. The maximum leverage allowed is also higher at 25x. Here you will find lots of perpetual contracts to trade. Notable coins traded here include Bitcoin, Ether, Solana, and even other DEXs’ native tokens such as UNI and SUSHI, among many others.
Learn more about dYdX here:
How to Trade Crypto on dYdX
Does this sound overly complicated? It actually is pretty simple in practice! Now we’ll demonstrate in a short step-by-step guide on using dYdX.
Note that dYdX is a place where you can try decentralized margin trading rather than swap crypto assets to use in your crypto wallet. Think of it as a decentralized version of the stock exchange, but with crypto as the underlying assets.
Step 1. Go to the dYdX website.
Simply head to the dYdX exchange.
Step 2. Click on Trade.
You’ll find the Trade button in the upper-left corner of your screen.

Step 3. Connect your crypto wallet.
To do this, click on Connect wallet.

Follow the on-screen instructions to verify you can use this wallet. This step just means to ensure you are not abusing someone else’s crypto wallet.
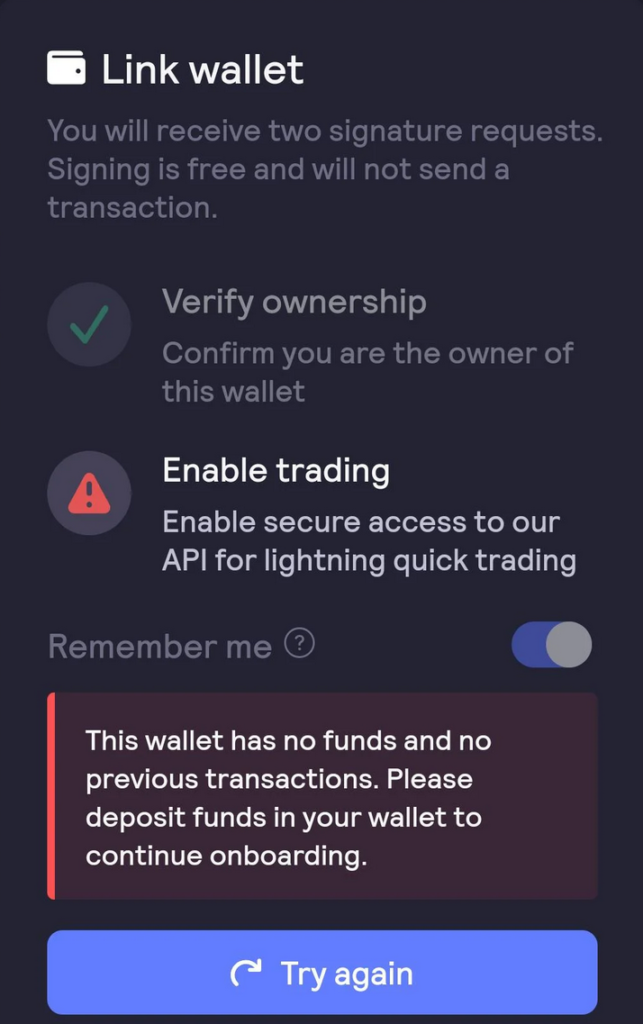
Step 4. Deposit funds to dYdX.
The DEX will want you to carry out a separate transaction for depositing the crypto you’d like to exchange. Just select Deposit from the bottom of the menu on the left.
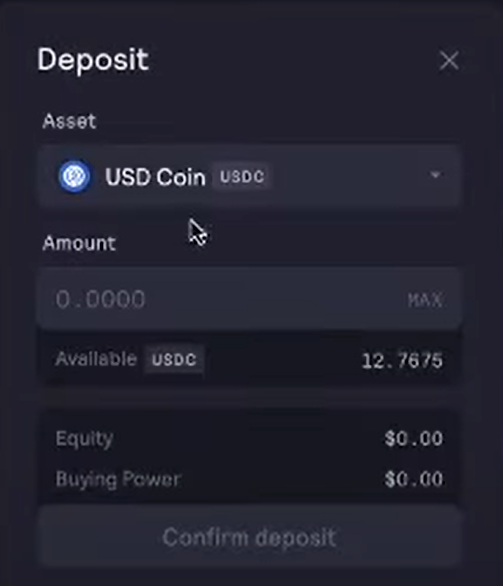
In the window that opens, choose the base cryptocurrency and amount to spend, then click on Confirm deposit.
Step 5. Make your trade.
Navigate to the Trade tab up top.

If you click on All markets, you’ll see a list of assets to trade. Choose the one you want.
Now you should see the selected pair of assets and some options as to what you can do.
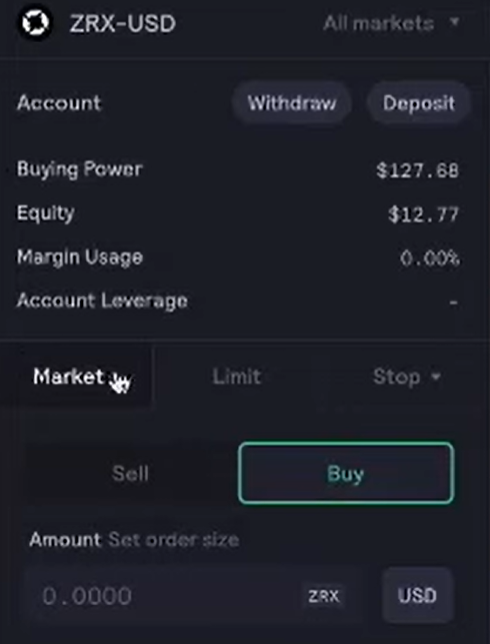
More specifically, you can place Market, Limit, or Stop limit orders with this asset.
- Market orders use the price at the time of placing the order;
- Limit orders require you to input your desired price for the transaction to occur. It won’t be executed until this level is reached;
- Stop limit orders take the process one step further. They ask that you specify a trigger price, at which the transaction becomes a Limit order (so you have to set your desired price too).
Note that the Buy and Sell tabs here just specify whether you’re choosing a short or a long position. Pressing them will not execute the trade.
Instead, you’d need to click on Place Order at the bottom of the menu to confirm.

3. PancakeSwap

Another well-liked and widely-used decentralized exchange is PancakeSwap. As you can tell by its name, this DEX works in essentially the same way as UniSwap. However, there is one notable difference.
Where UniSwap is an Ethereum protocol, PancakeSwap runs on the BNB blockchain instead. Build and Build, which used to be known as the Binance Smart Chain, is — you guessed it! — Binance’s own blockchain.
Indeed, the tech giant that is Binance has plenty of DeFi solutions under its sleeve, despite being primarily known as a CEX. In fact, Binance invented its own standard for classifying crypto tokens — BEP20. It competes with the Ethereum-based ERC-20 and ERC-21.
PancakeSwap, thus, appeared to offer services akin to UniSwap’s but for the BEP20 ecosystem.
How Does PancakeSwap Work?
The mechanism behind PancakeSwap is extremely similar to Uniswap’s. Investors can lock their tokens in liquidity pools, from which traders then borrow. At the same time, liquidity providers earn from transaction fees.
In addition, PancakeSwap users can also stake their tokens to participate in farming pools. This, over time, will earn them additional income, plus CAKE tokens. CAKE is the governance token that allows holders to make decisions about the future of the PancakeSwap protocol. CAKE tokens themselves can also be staked.
Not sure whether you should use Uniswap or PancakeSwap? Check out this comparison video by CoinMarketCap:
How to Exchange Crypto in PancakeSwap
Exchanging between Binance-based cryptocurrencies with PancakeSwap is quite easy. The process is also very similar to using Uniswap.
Step 1. Go to the PancakeSwap website.
Head over to the DEX’s site and choose Trade — Swap from the main menu.

Step 2. Connect your crypto wallet.
You should now see this window on your screen:

Click on Connect Wallet. You’ll have several options to choose from.
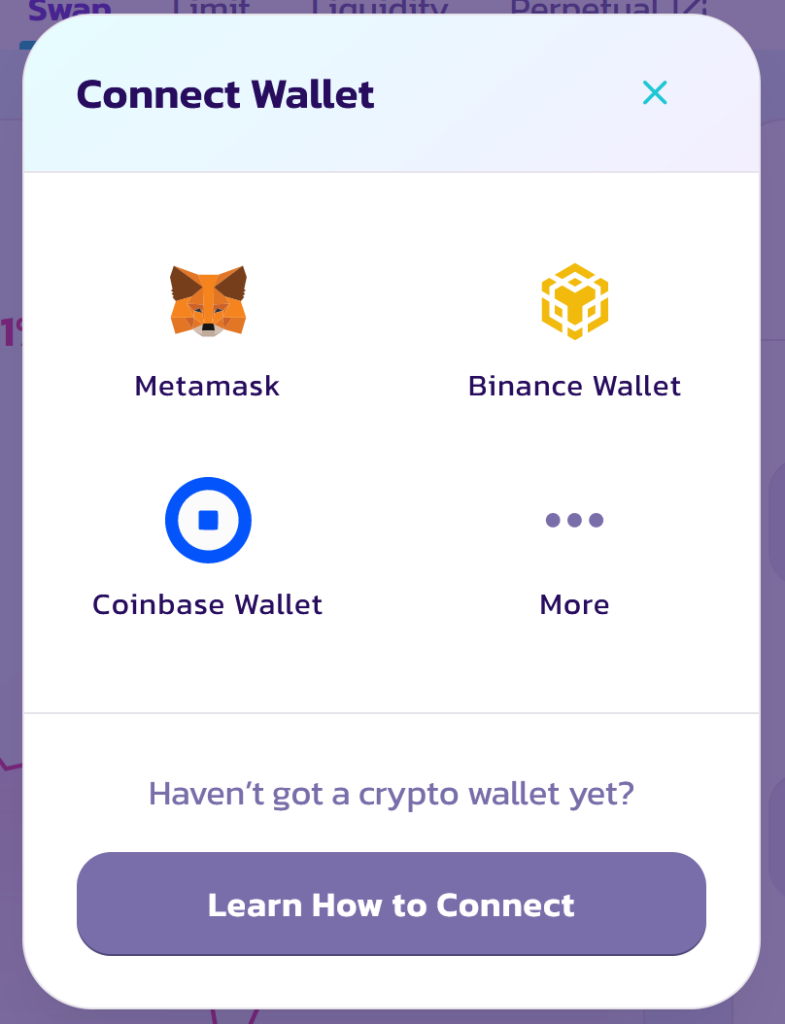
Select the one that applies to you and follow the instructions to link your wallet to PancakeSwap.
Step 3. Set up your swap transaction.
Choose the currencies you want to swap from and to. Then, enter the amount you want to convert in the From field. PancakeSwap will automatically calculate how much of the other cryptocurrency you’ll get.
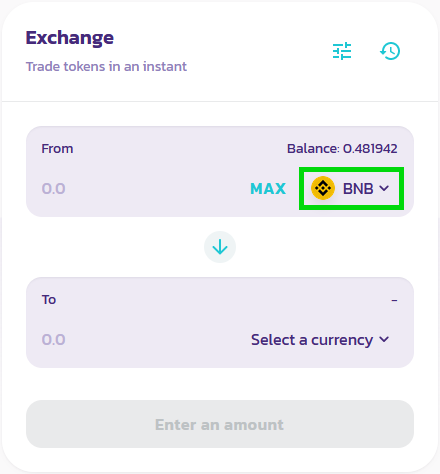
Step 4. Place your order.
When you have both of your cryptos and amounts selected, press Swap to order the exchange.

Step 5. Confirm the trade.
You’ll get one last chance to look over everything before you commit. If all looks good, click Confirm Swap. That’s all!

4. Curve Finance

Innovation meets elegance in one of DeFi’s finest: Curve Finance. Curve is a DEX running on the Ethereum network that bears many similarities to Uniswap. The most significant difference is that Curve aims to provide better trading conditions by being more selective with its asset listings.
Indeed, Curve Finance forms liquidity pools based on similarities to minimize the costs for the user. For example, it has liquidity pools for stablecoins, wrapped assets, etc. Using this ‘birds of a feather fly together’ maxim, this DEX prioritizes price stability over volatility.
Curve Finance classifies itself as an ‘automated market maker,’ or an AMM. Though this term sounds fancy, in practice, it refers to the use of liquidity pools that we already covered. In fact, Uniswap is also an AMM, technically speaking.
For more details about Curve Finance, check out this video:
How Does Curve Finance Work?
Liquidity providers use smart contracts to lock their crypto assets into liquidity pools. Then, everyone else can trade for tokens already in the LPs.
Curve’s programming includes a setting to encourage all LPs to rebalance all the time. As with other DEXs, each liquidity pool consists of equal amounts of two assets, say A and B. When a trader comes to exchange some of their own tokens and sells A to the pool, getting some B tokens in return, the two assets are in disbalance.
The LP will automatically lower the price of token A for a time. This would encourage A purchases, gradually restoring equilibrium to the liquidity pool.
Another interesting detail about Curve is that it aims to reduce impermanent loss. However, this is not always a benefit. Sometimes, such slippage can work out in favor of the user. Needless to say, the low volatility that is Curve Finance’s most outstanding feature is not everybody’s cup of tea.
How to Exchange Digital Assets in Curve
This section will show you how to swap cryptocurrencies using Curve’s liquidity pools. Though the text-heavy interface of Curve might seem intimidating, worry not! It’s a lot friendlier than you might expect at first glance.
Step 1. Navigate to the Curve Finance website.
Use your browser to go to Curve. You will be greeted by a somewhat retro-looking interface.
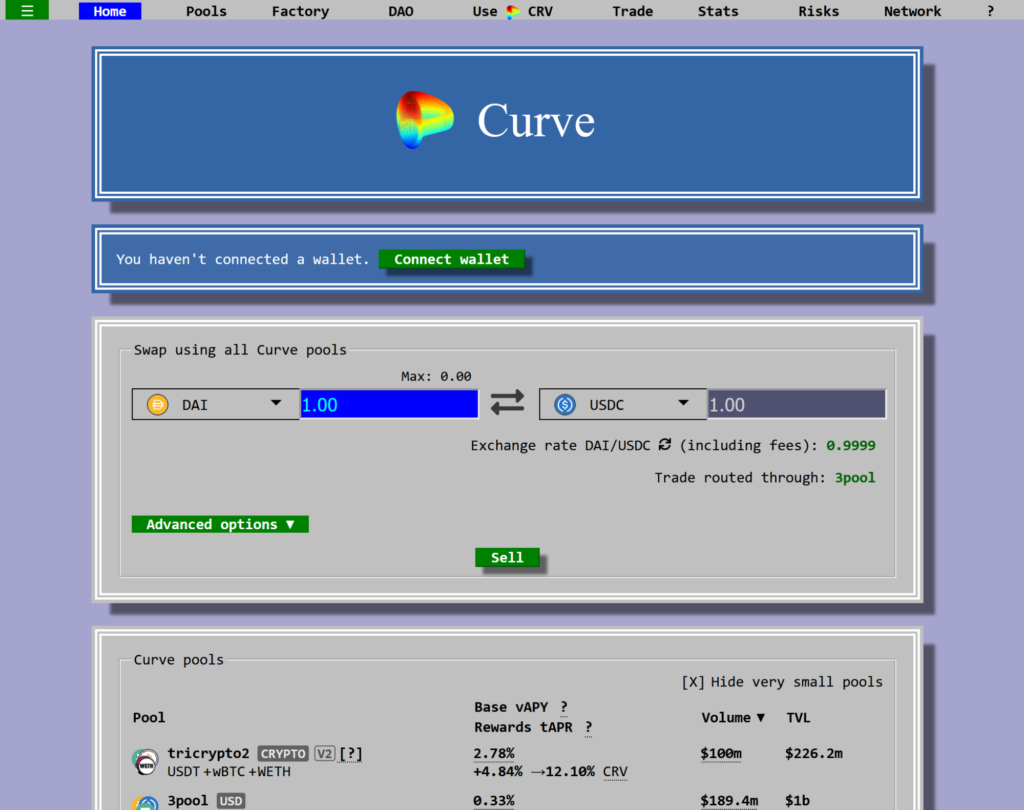
Step 2. Connect a wallet.
To make a swap, Curve needs access to your crypto wallet. Click on Connect Wallet.

Then, Curve will show you what wallets it supports:

Make your choice and complete the relevant steps to link your wallet.
Step 3. Choose the two cryptocurrencies you wish to swap.
Like with other DEXs, you have your From and To columns to set up the exchange.
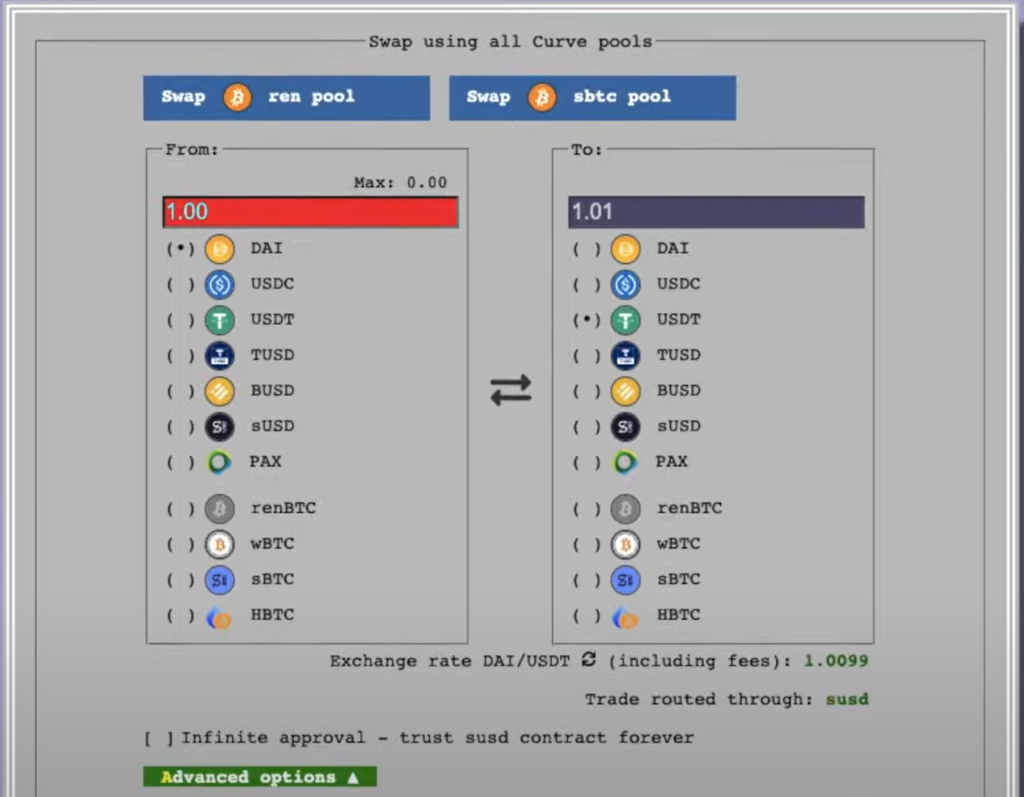
All you need to do is make sure to put the dot in the parentheses before the correct asset.
Though Curve uses multiple liquidity pools, it will automatically find the best exchange rate for the transaction and present the total exchange costs at the bottom right.
You can also mess around with the advanced settings if you have other requirements before placing your swap, but it’s optional.
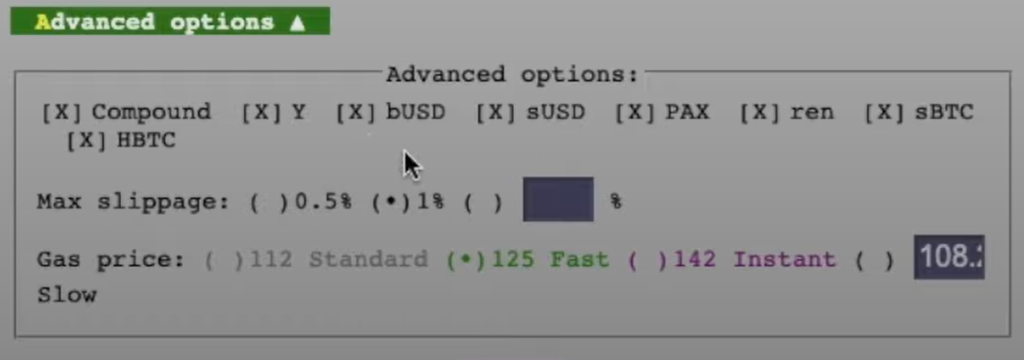
Step 4. Order the conversion.
Check that all of the info is correct, then click on Sell.
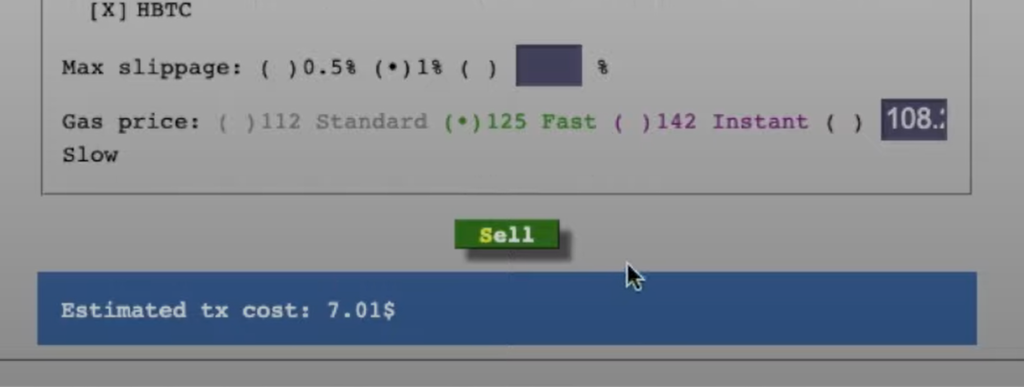
This completes the transaction. See, we told you it’s a lot simpler than you’d expect!
5. 1inch

Traders looking for maximum cost efficiency might be huge fans of 1inch. That’s because this DEX is of the aggregator type and claims to offer the best pricing.
As we mentioned earlier in our discussion of DEX types, aggregators pull data from other exchanges. Thus, 1inch compares the current exchange rates available on several DEXs to find the best one for your order. In fact, one of the many DEXs 1inch incorporates is Uniswap, which we already talked about.
What’s more, the algorithm also accounts for gas fees and any other expenses involved. The code is so sophisticated that it can even split up one transaction into several smaller ones to minimize fees. It does all that by itself, so even if it sounds complicated, the process is surprisingly beginner-friendly in practice.
The 1inch aggregator runs on the Ethereum blockchain. However, it’s also integrated with other blockchain networks (e.g., BNB, Avalanche, Gnosis Protocol, etc.).
It still has a tiny market cap, but it’s the most popular DEX aggregator, so we wanted to include it to show you a different approach.
How Does 1inch Work?
Have you ever gone on websites that compare airplane ticket prices? Train tickets, hotels? They display various listings that match your search parameters and allow you to make a booking directly. Those websites are aggregators, too, just like 1inch!
In terms of methodology, you need to know two aspects of 1inch.
First, there’s the aggregation protocol. This refers to 1inch’s ability to find both the best exchange rate and the lowest gas fees for a transaction. In fact, the DEX can also split the transaction across different exchanges if that will lower the gas fees. To get the most optimal exchange rate, it may even perform other conversions along the way instead of a direct trade between A and B. Its code is truly ingenious as it knows how to secure lower fees for the user within a single transaction.
In addition, 1inch also has liquidity pools. They work just like on other DEXs. Thus, you can execute trades directly within 1inch if its own liquidity pool offers the best rate at the time. Then, the transaction is a simple swap like with Uniswap or PancakeSwap.
Still curious? Find out more about how the 1inch aggregator works here:
How to Exchange Crypto on 1inch
Now that you know a thing or two about 1inch, it’s time to see how converting crypto works on this decentralized exchange.
Step 1. Go to the 1inch website.
Simply open your browser and navigate to 1inch. Most likely, the address will immediately route you to the swap page, where you can place an exchange order.
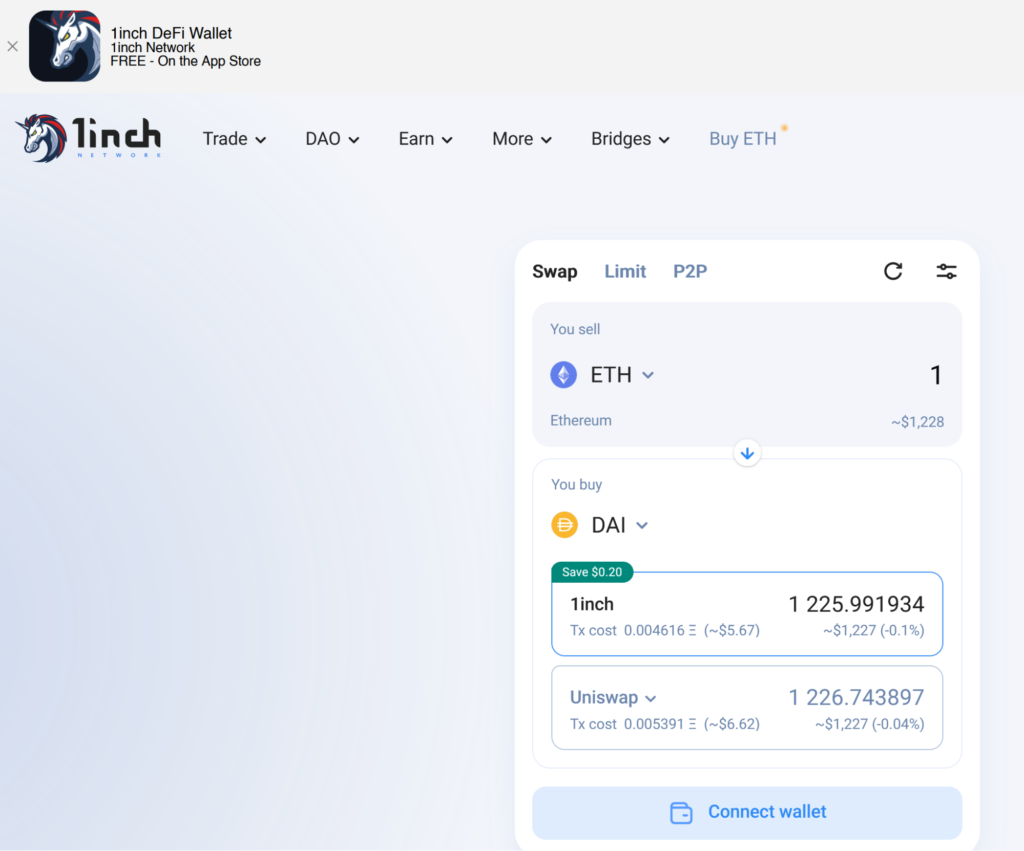
Note that you also have limit order and peer-to-peer trading available in the same menu. We won’t get into those orders now, but it’s good to know the options are there.
As with other DEXs, you can’t really do much without a crypto wallet. This brings us to the next step.
Step 2. Connect your crypto wallet.
Press the Connect wallet button. In the window that opens, check that you read and accepted the terms and privacy policy of 1inch. This would unlock the next two mini-steps.
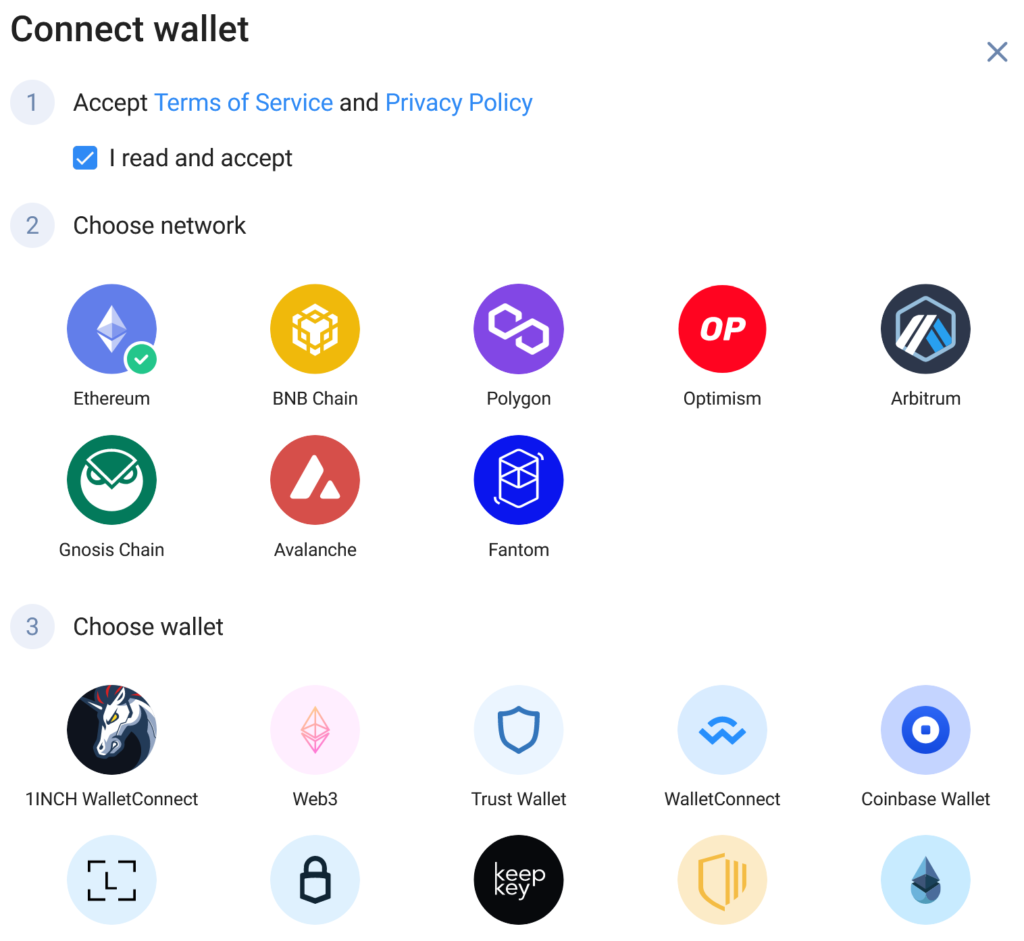
Then, choose the blockchain network and wallet that you intend to use. As soon as you select a wallet, you’ll get additional instructions to verify your identity and link that wallet to 1inch.
Step 3. Set up your swap order.
With your wallet connected, you’re ready to exchange cryptocurrency.
- Under You sell, select the crypto you want to use and the amount to exchange.
- Under You buy, choose the cryptocurrency you want to convert to. 1inch will automatically calculate how much of it you can get based on the currency exchange rate and gas fees.
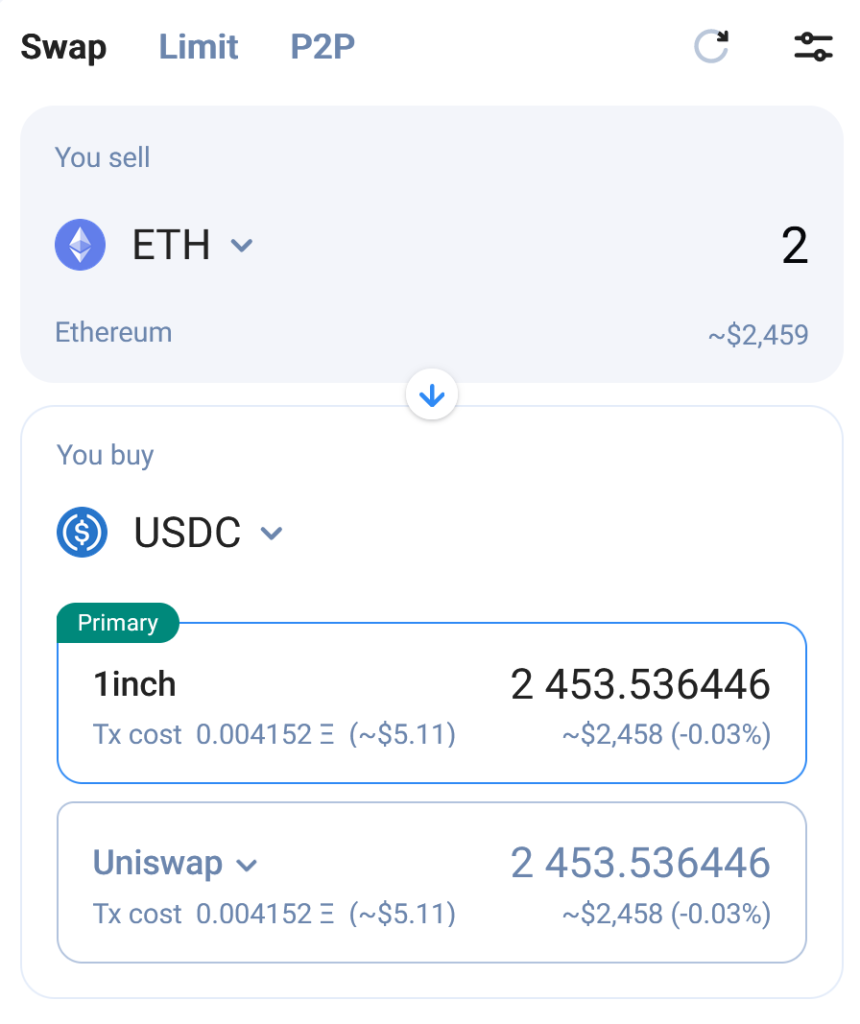
Step 4. Perform the swap.
When you’re ready, click on Give permission to swap.

Adjust the swap settings if necessary, and press Confirm swap to finalize the transaction.
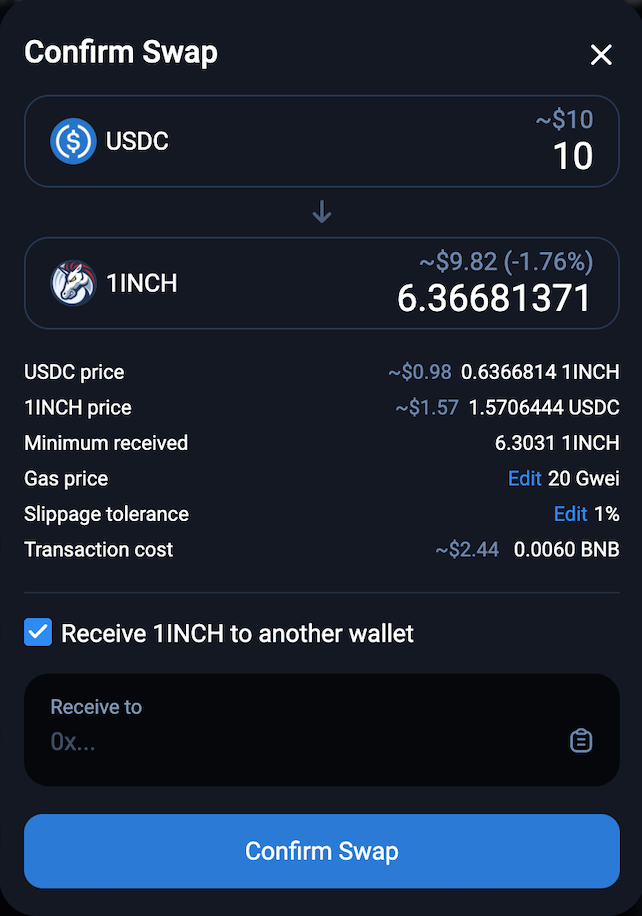
That’s all it takes! Your new crypto tokens should now be in your wallet.
UniSwap, DYDX, PancakeSwap, Curve, 1inch: A Comparison
Are you still having trouble making out the differences between these decentralized exchanges? Here is a brief overview of their features to help you decide which DEX might be the most suitable for your needs.
| Factor | Uniswap | dYdX | Pancakeswap | Curve | 1inch |
| Type of DEX: | Swap | Order book | Swap | Swap | Aggregator |
| Market share: | 0.0015% | 0.0007% | 0.0004% | 0.0004% | <0.0001% |
| Trade volume (24h): | $1.1 billion | $560 million | $337 million | $290 million | $994K |
| Founded in: | 2021 | 2019 | 2020 | 2020 | 2019 |
| Blockchain: | Ethereum | Ethereum (L1), StarkWare (L2) | Binance | Ethereum | Ethereum; compatible with BNB, Polygon, Gnosis, Avalanche, Optimism, Arbitrum, Fantom. |
| Best for trading: | ERC coins and tokens | Derivatives:Margin trading; perpetual contracts | BEP coins and tokens | Stablecoins, wrapped tokens | Coins and tokens running on various blockchains |
| Liquidity pools? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Frequently Asked Questions About DEXs
Looking for a quick answer to your most pertinent DEX-related questions? We got you! You can find the TL;DR on decentralized exchanges in this section.
What Is a Decentralized Exchange and How Does It Work?
Decentralized exchanges are marketplaces where people can go to turn one cryptocurrency into another. They are like a moneychanger’s office for crypto — except there is no middleman. Instead, decentralized exchanges rely on blockchain technology to facilitate all transactions. They most commonly use liquidity pools or order books to create price listings and ensure liquidity to traders. All decentralized exchanges work with crypto only and do not accept fiat currency.
Is a DEX Different from a Decentralized Exchange?
No, they’re the same thing! The name DEX is just less of a mouthful.
How Do Decentralized Exchanges Make Money?
Like traditional exchanges or brokers, DEXs charge fees on each transaction. Though these may be modest in most cases, the high transaction volume ensures that decentralized exchanges remain profitable over time.
Is it Legal to Use a Decentralized Exchange?
Generally speaking — yes. However, with the general push towards more regulation in the booming cryptocurrency sector, regulatory commissions have their eyes on decentralized exchanges. You should check what crypto use, trading, and exchanging laws are like in your country. Note that while a DEX might be accessible from your location, that’s no guarantee that it is legal.
Can Decentralized Exchanges Be Hacked?
In theory, any piece of code can be hacked. In this sense, decentralized exchanges are no exception. Nevertheless, DEXs do not hold or control any of the funds associated with their use. Thus, it’s not like a hacker can just burst into the digital vault of a DEX to rob it. It would also be quite difficult to find the data of users of the DEX and worm into their wallets because decentralized exchanges don’t collect customer data. Still, we have seen decentralized exchanges get hacked before. It can happen when hackers identify a weakness in the code of the DEX. But with each successful hack, such flaws are removed, and all newer exchanges have learned from the mistakes of their predecessors. So, these exploitable bugs get fewer and fewer.
Is Coinbase a Decentralized Exchange?
No, Coinbase is a centralized exchange (or CEX). In many ways, it’s quite the opposite, though it aims to fulfill the same function.
Is Using Decentralized Exchanges Safe?
It’s generally safe. However, bear in mind that crypto trading is a risky activity, especially if you trade on a margin. Always do your own research first and make sure you understand the risks before making trading decisions. Also, keep your private keys safe — sharing your crypto wallet address online is risky.
Do You Need KYC for a DEX?
No. KYC or “Know-Your-Customer” are rules that require companies to collect data about their users. Decentralized exchanges, however, are anonymous. Thus, they don’t collect or store data about the identities of their customers. Unlike centralized exchanges, they don’t require an account.
Do You Need a Centralized Exchanges Account to Access a DEX?
No, you don’t need an account. However, some centralized exchanges, such as Coinbase, offer wallets you can use on a DEX.
Conclusion
Decentralized crypto exchanges are digital marketplaces where people go to either convert crypto coins for personal use or trade them competitively for profit. Part of the DeFi sphere, they offer an intermediary-free way for people to manage and diversify their crypto wallets.
In this guide, we demonstrated that there are several types of DEXs and a great many choices in each category. We introduced you in more detail to some of the industry’s favorites — Uniswap, dYdX, Pancakeswap, Curve, and 1inch. These exchanges fulfill slightly different functions, each with its own unique set of advantages.
Remember that one DEX is not necessarily better than the rest; it’s all about your needs and preferences. Considering how versatile the world of decentralized exchanges is, we are more than certain you will find a DEX that works for you. And when that happens, you can unlock your true potential as a crypto investor or trader. Good luck!

